Get your Prostatitis Treatment strategies in the following paragraphs.
Prostatitis is defined as microscopic inflammation of the prostatic tissues, which can be manifested by myriad clinical symptoms. Recently, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has proposed a new classification for prostatitis ( prostate infection ):
If you want to have presonalised health answer for as little as 5 usd from a real doctor Click Here now
l- Acute bacterial prostatitis lll- Chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
• Inflammatory• Non-inflammatory
IV- Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis
Both, the acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis are recognized by presence of bacterial infection in prostate gland. Therefore,prostatitis treatment is variable and it really depends mainly on the type and cause of prostatitis .
Usually, acute and chronic bacterial treatment is with antibiotics. In severe cases, the patient will receive intravenous injections of antibiotics in the hospital. After case improvement, oral antibiotics course will be continued for 14-30 days to prevent relapses.
Mostly, the duration of antibiotic course for chronic bacterial prostatitis is longer than acute bacterial prostatitis; it may be repeated several times as well.
If you are suffering from acute bacterial prostatitis, your doctor will advise you to take tetracycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) or quinolone drugs.
Common antibiotics used for acute bacterial prostatitis treatment are:
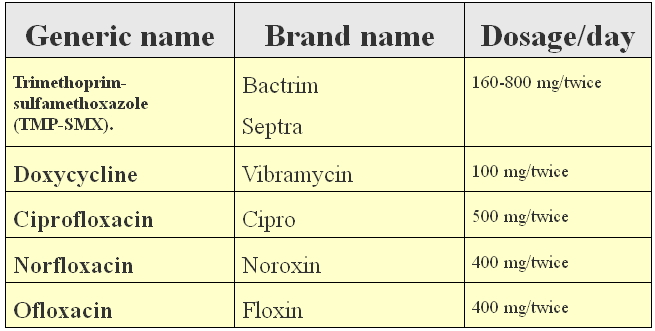
Other antibiotics used in acute bacterial prostatitis include: Miostat (carbenicillin), Ancef (cefazolin), Keflex (cephalexin), Velosef (cephradine), and Minocin (minocycline).
The effectiveness of treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is restricted due to the fact that most antibiotics can’t penetrate the intact prostatic epithelium when it is un-inflamed. Therefore, the more lipophilic antibiotics (having an affinity for lipids or fat-loving), the better will be the treatment.
However, the drug of choice in the treatment for prostatitis is TMP-SMX. If it fails, your doctor will try fluoroquinolone. In rare cases, transurethral prostatectomy surgery can be performed to remove the entire infected prostatic tissue.
Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain
Clinically, it is estimated that more than ninety percent of all men suffering from prostatitis show symptoms of chronic nonbacterial prostatitis/ chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CNP/ CPPS).
Actually, this type of chronic prostatitis treatment is very difficult and challenging, including:
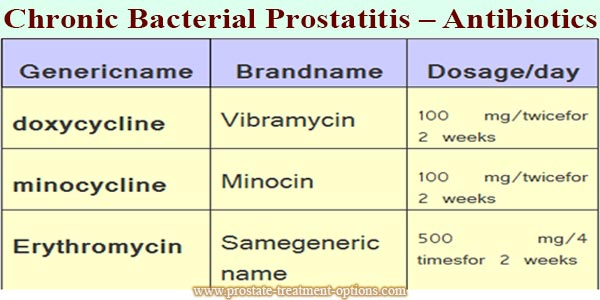
Antibiotics
The most commonly used antibiotics are
Alpha blockers
This type of treatment helps in the relaxation of the bladder neck, as well as the muscles surrounding the bladder, thus relives the associated prostatitis symptoms , especially pain
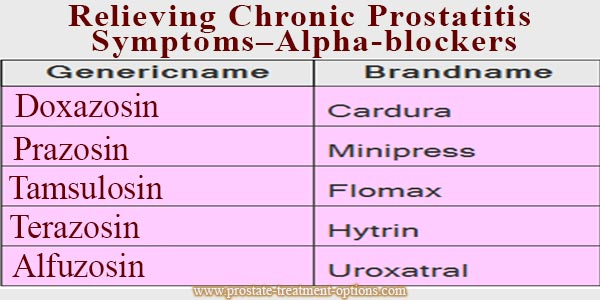
Main adverse reactions of alpha-blockers include hypotension and headache.
Analgesics
Certain pain relievers such as aspirin and ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) can make the patient feel more comfortable, but multiple uses of these drugs can cause a lot of side effects, such as abdominal pain, ulcers and intestinal bleeding.
There are myriad of untested prostatitis treatment, like biofeedback, muscle relaxants, as well as some other relaxation techniques.
Some experts recommend transurethral microwave thermotherapy or some home remedies like hot sits baths to relief symptoms.
Asymptomatic Prostatitis
Usually, asymptomatic prostatitis treatment is by taking antibiotics for 2 weeks or until prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test is normal again, as asymptomatic prostatitis is known to increases PSA levels.
Related topics:
- Why you should go for Prostatitis Diet?
- Find out the hidden secrets of Prostatitis Cures apart prostatitis treatment!